Electrical
Electric-Arc Flash Hazards
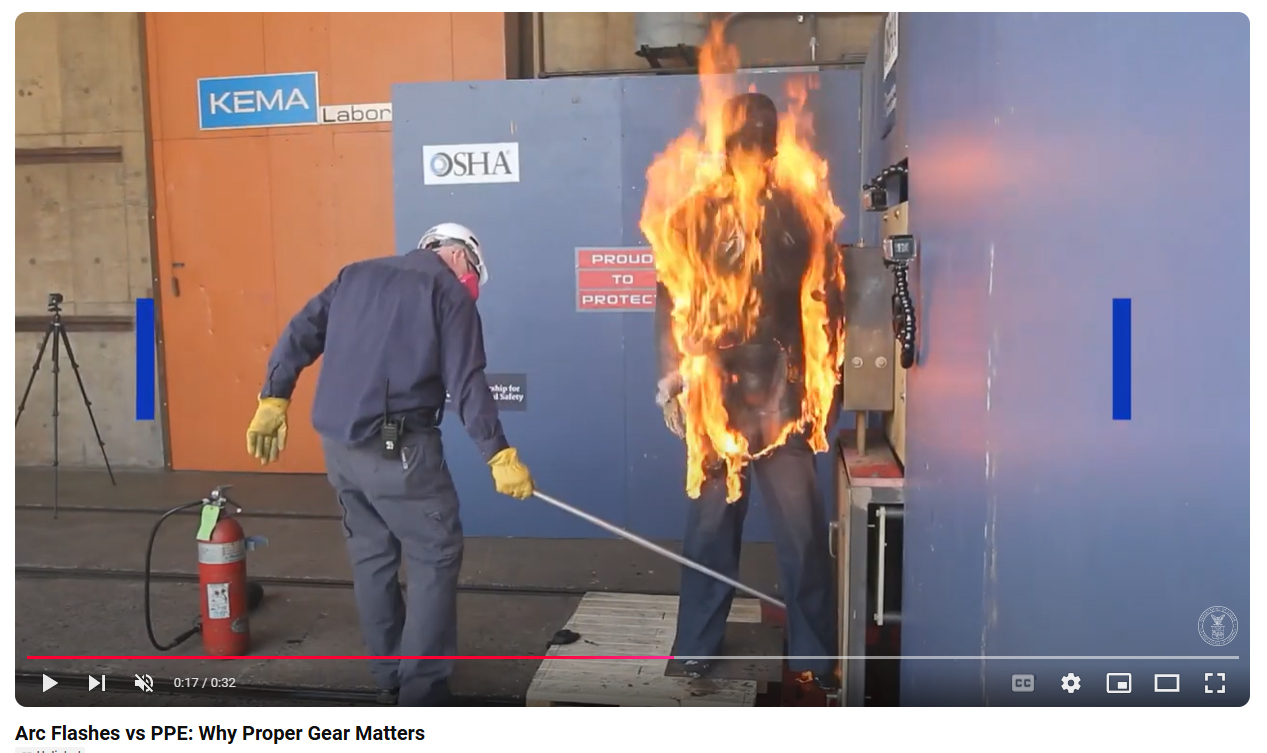
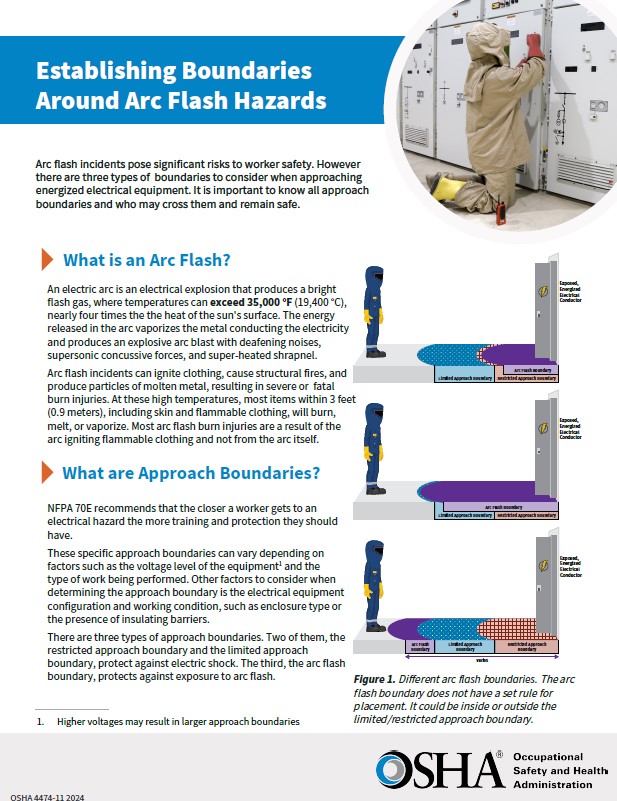
An electric arc is a type of electrical explosion. The electric arc produces a bright flash of hot gas, where temperatures can exceed 35,000 °F (19,400 °C), nearly four times the heat of the sun’s surface. The energy released in the arc rapidly heats and vaporizes the metal conducting the electricity, producing an explosive arc blast resulting in deafening noises, supersonic concussive forces, and super-heated shrapnel.
Most arc flash burn injuries are a result of the arc igniting flammable clothing and not from the arc itself.
Flammable Clothing vs Appropriate Arc Rated PPE (AR PPE)
Special thanks to KEMA Laboratories and the Partnership for Electrical Safety for this testing footage
OSHA has produced the following guides to assist employers and employees in understanding and protecting against arc flash hazards:
For Employers
For Employees
Additional Resources
- NFPA 70E. NFPA 70E requirements for safe work practices to protect personnel by reducing exposure to major electrical hazards. Originally developed at OSHA's request, NFPA 70E helps companies and employees avoid workplace injuries and fatalities due to shock, electrocution, arc flash, and arc blast, and assists in complying with OSHA 1910 Subpart S and OSHA 1926 Subpart K. (viewable for free with NFPA account registration)
- Partnership for Electrical Safety. The Partnership for Electrical Safety (PES) believes that every American working on or near energized electrical equipment deserves equal protection from arc flash, including the appropriate arc rated clothing and associated personal protective equipment (PPE). PES seeks to educate those at risk and to make plain to relevant oversight entities the need for use of PPE when doing industrial electrical work, and the extreme human and financial costs of non-compliance.