Lead: Battery Manufacturing eTool
Plate Processing » Enveloping and Wrapping

Enveloping involves placing a plate (usually positive), either automatically or manually, within porous membranes. The major sources of exposure in this process result from lead oxide being released when the plates are handled incorrectly, such as resting them against the body or handling them in unventilated areas.
Potential Sources of Exposure

-
Lead oxide may become airborne due to workers improperly handling plates at the feed and discharge ends of enveloping machines as well as from the bellows effect when handling unsealed envelopes.
-
Exposure to lead may occur when the lead oxide that has accumulated on equipment, racks, and floors becomes airborne.
-
Lead dust may become airborne when workers improperly handle scrap plates.
-
Lead may contaminate clothing when a worker leans against contaminated equipment.
-
Increased exposure to lead oxide may occur when tamping plates in unventilated areas, such as the rack, creates puffs of lead dust.

Possible Engineering Controls

-
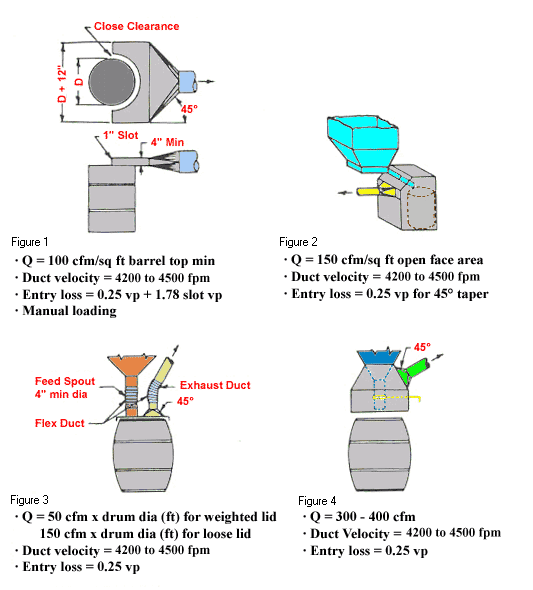
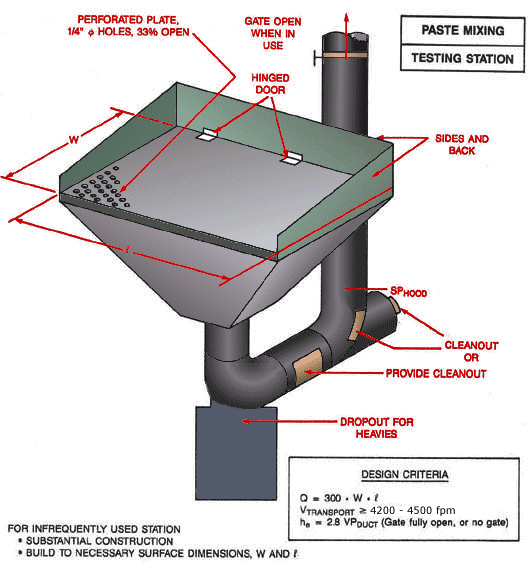
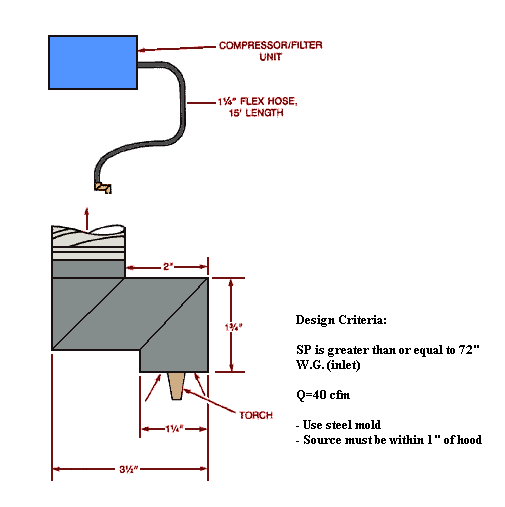
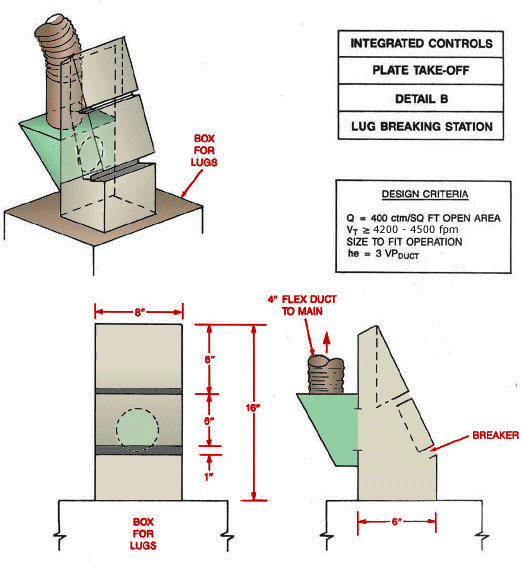
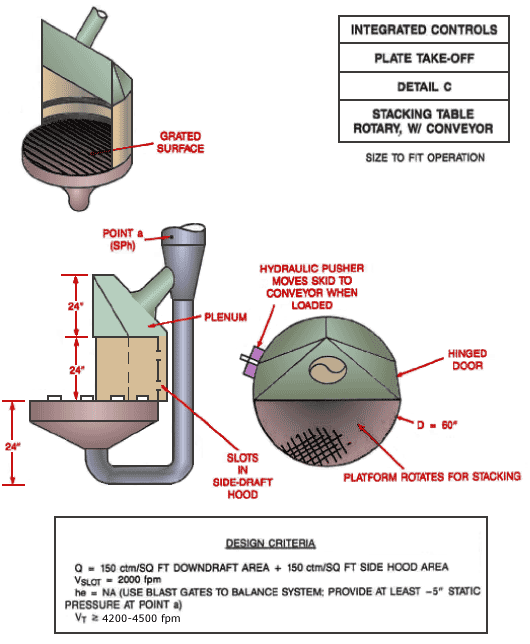
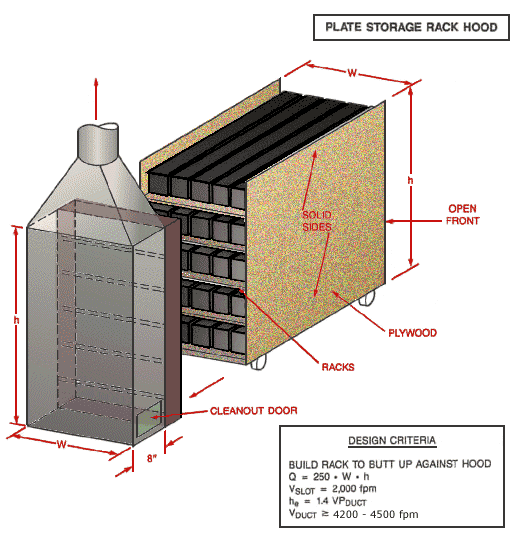
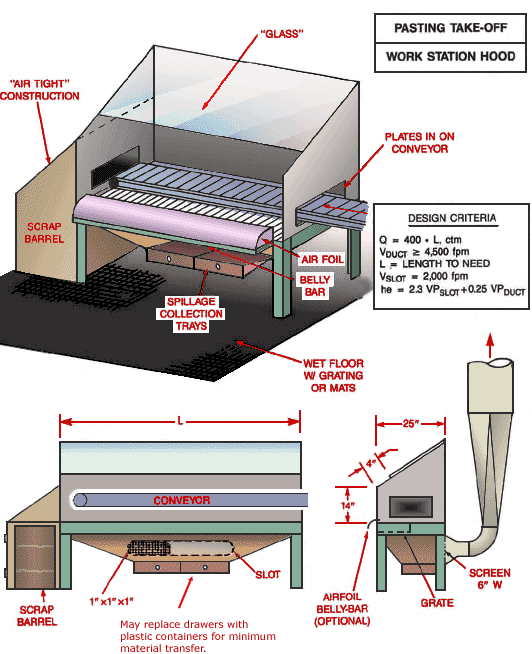
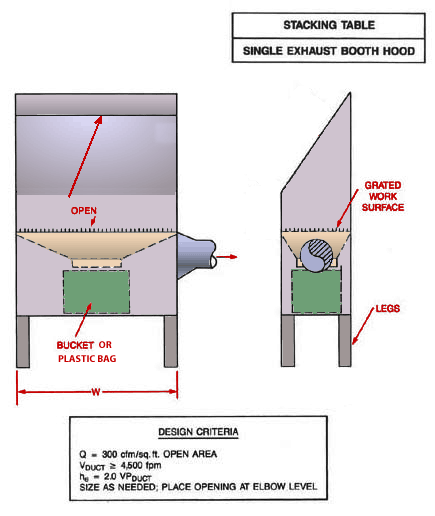
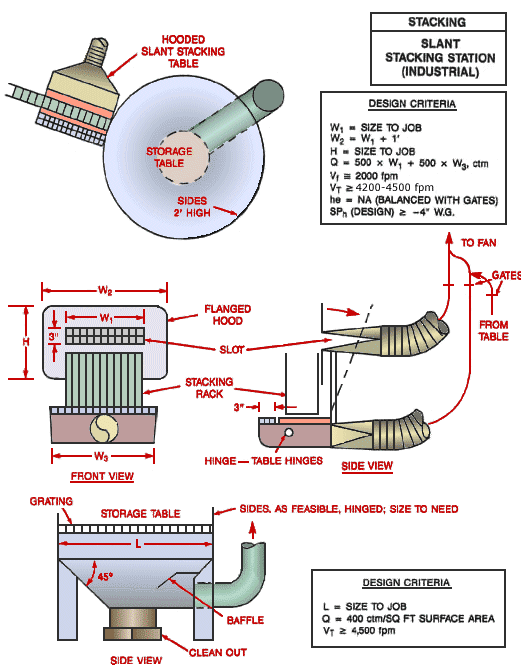
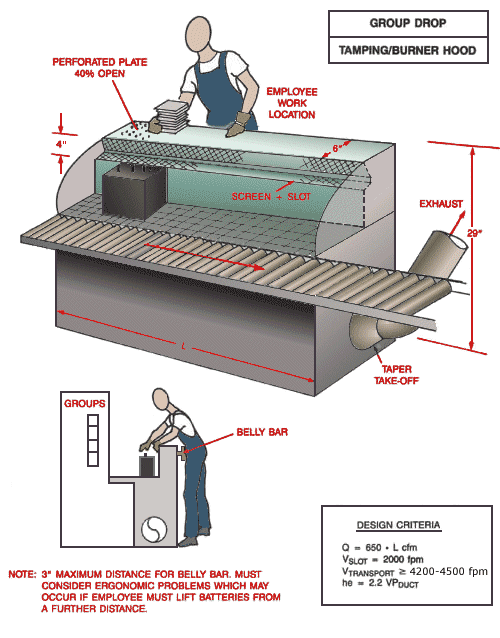
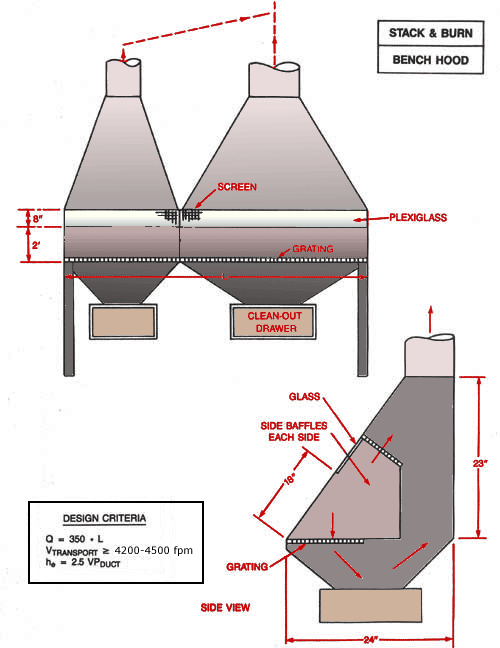
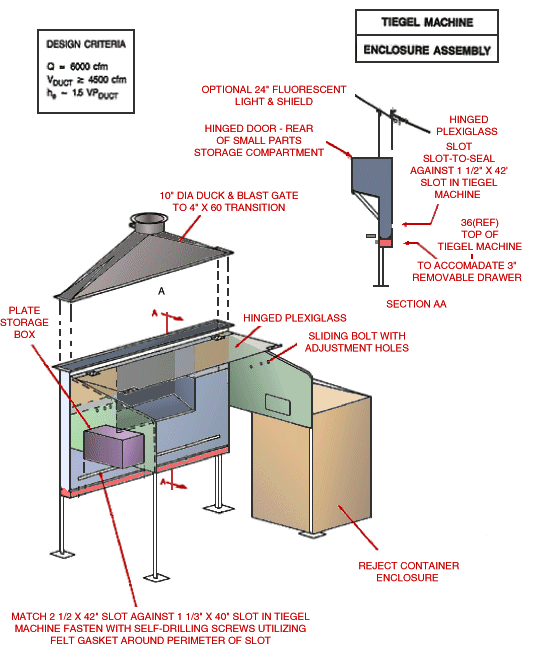
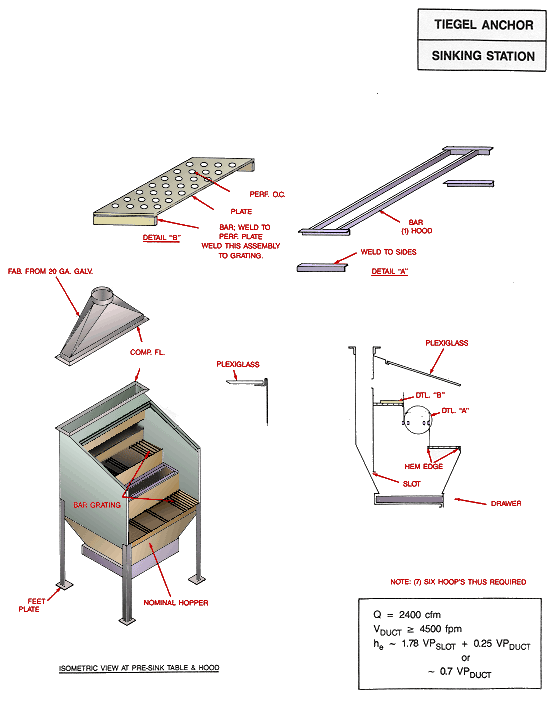
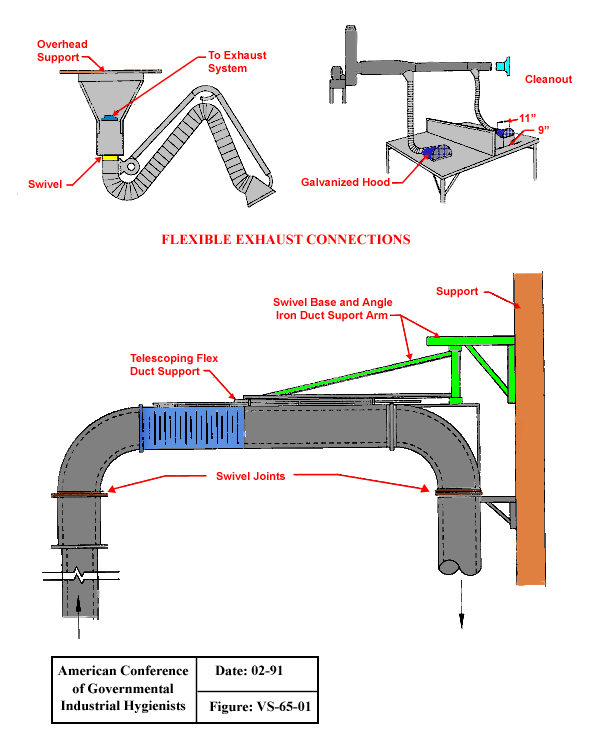
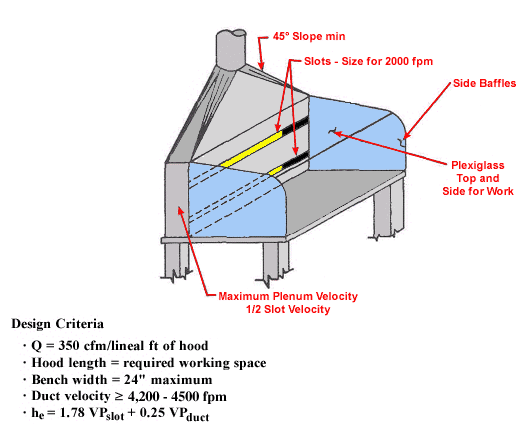
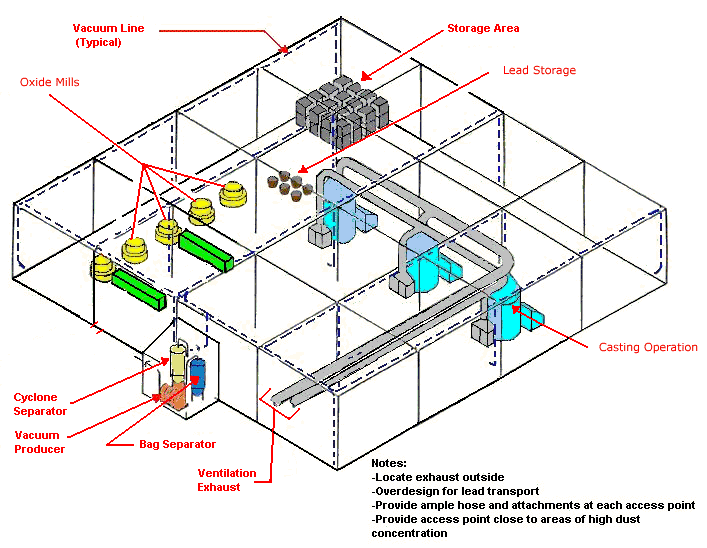
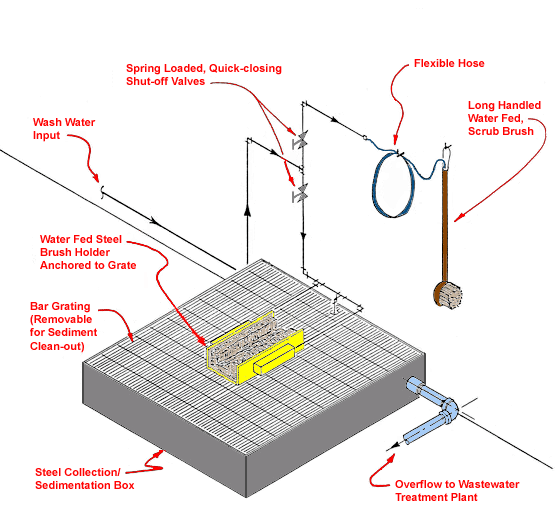
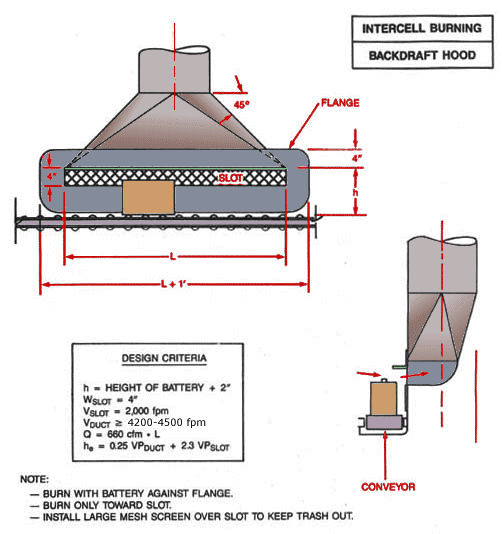
Use local exhaust ventilation, such as a grating or a perforated plate tamping stand that is equipped with downdraft and side-draft ventilation (Figure 4).
-
Enclose and ventilate equipment.
- Use a ventilated scrap barrel.
-
Provide a vacuum drop at the workstation.
-
Use a rotating base for placing pallets of plates so employees do not have to reach across.
-
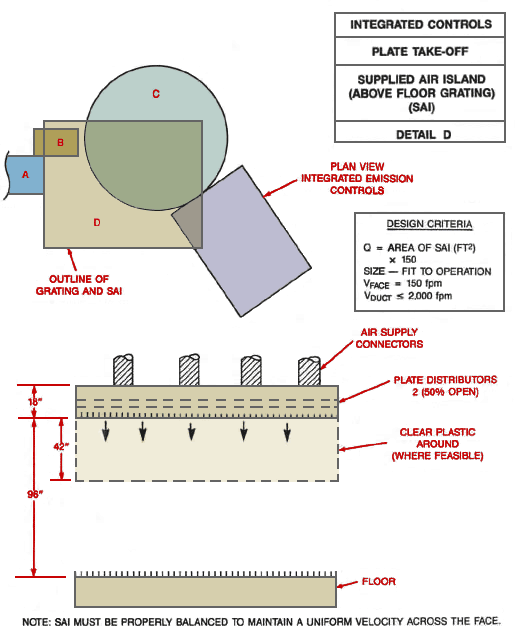
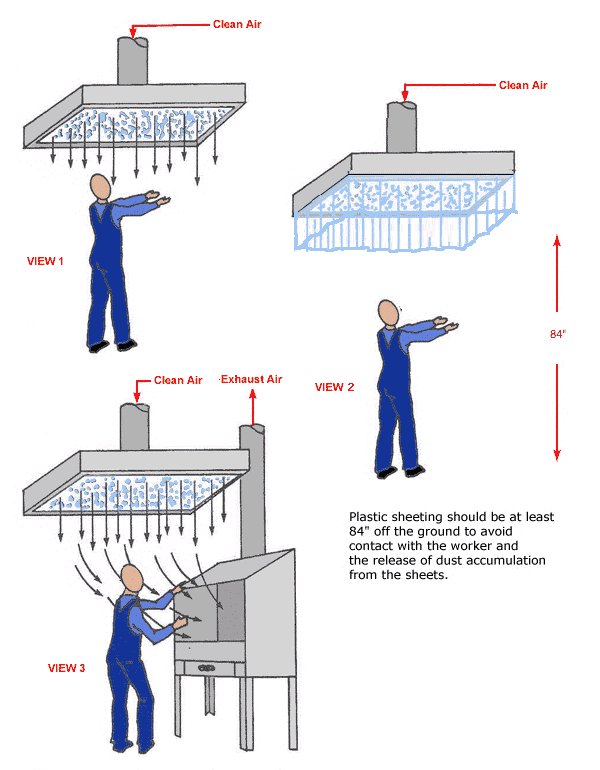
Use a laminar flow (supplied-air) island over operators workstation.

Possible Work Practice Controls
- Tamp plates carefully over ventilated work station.
-
Do not bang plates excessively while tamping.
-
-
Keep open ends of envelopes away from the face.
-
Handle groups of plates with hands only rather than leaning them against the stomach.
-
Wear an apron (Figure 2).
-
Place, do not throw, defective plates into a scrap barrel.
-
Cover drums with a plastic bag before removing them from the area.
-
Seal all doors, windows, and other openings on the enveloping machine.
-
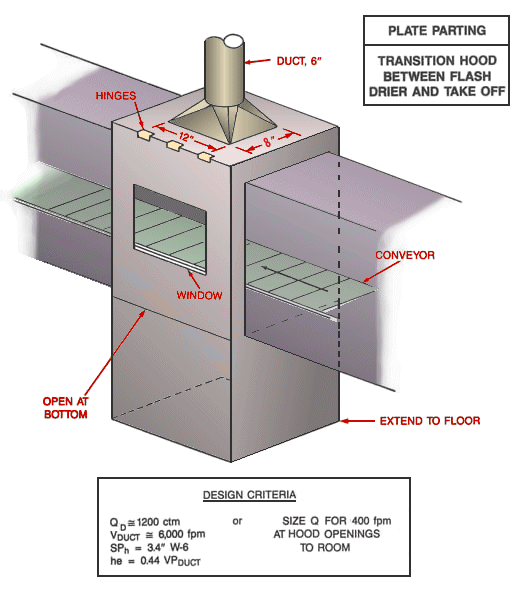
Perform plate parting using local exhaust ventilation (downdraft or side-draft), and not while the plates are moved from the pallets to the enveloping equipment.
-
Do not store plates on ventilated tamping stands.
-
Provide adequate PPE, a change of clothes, and shower rooms (see OSHA Lead Requirements for PPE, Housekeeping, and Hygiene Facilities).
- Maintenance:
-
Ensure that local exhaust ventilation is working properly.
-
Prevent cross drafts.
-
Use plastic bags in catch receptacles to facilitate removal without dust generation.
-
- Housekeeping:
-
Vacuum the separator boards, workstation, and adjacent areas.
-
Use dust suppression techniques, such as keeping the floor wet, using dust suppression compounds, or vacuuming.
-
Ensure plate trays are vacuumed clean.
-

With video exposure monitoring (VEM), worker exposures to lead are monitored and recorded with a direct reading instrument. At the same time, workplace activities are recorded on a videotape. The left hand bar indicates changes in total dust concentrations over time.
As the employee removes plates from the pasting machine and brushes the edges of the plates, the red bar indicates increasing employee exposure to lead dust.
Note: This example illustrates how VEM can be used for determining sources of employee exposure. Other sources of employee lead exposure can be determined by using VEM sampling for a full work shift.