Poultry Processing Industry eTool
Plant-Wide Hazards » Other OSHA Requirements & Programs
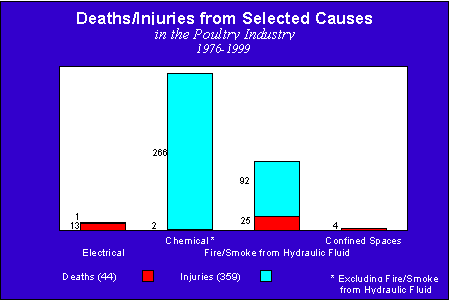
In addition to the workplace hazards that contribute to the predominant types of injuries and illnesses identified in the 1997 OSHA Survey of the Poultry Processing Industry, there are other hazards that are subject to OSHA standards and requirements.
Three of these hazards are highlighted in this module because of their potential for serious injury or illness or fatalities. These hazards are:
Other OSHA standards that are important for the control of hazards in the poultry processing industry are:
- 29 CFR Part 1904 Recording and Reporting Occupational Injuries and Illnesses,
- 29 CFR 1910.95. Occupational noise exposure,
- 29 CFR 1910 Subpart I: Personal Protective Equipment (including 1910.134. Respiratory Protection), and
- 29 CFR 1910.151. Medical services and first aid.
NOTE: Employers in states with state-run safety and health plans should check with their state agency. Their state may enforce standards that, while "as effective as federal standards," may not be identical to the federal requirements
The user of this module is encouraged to consult these standards directly. In addition to the standards themselves, OSHA has produced a number of publications on these topics available online or as printed copies by ordering online or by phone, fax or mail.
On November 15, 2007, OSHA published a final rule that stipulates that the employer must pay for required personal protective equipment, except in the limited cases specified in the standard. Safety-toe protective footwear and prescription safety glasses were excepted from the employer payment requirement, in large part because these items were considered to be very personal in nature and were often worn off the jobsite.